

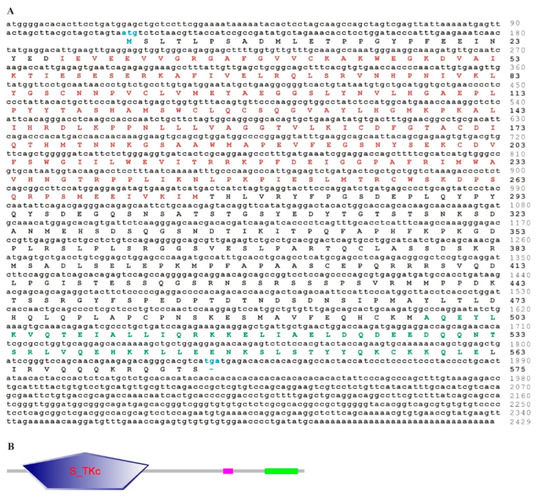
Yellow colour in diagram present this different residues of the protienĪla, arg, tyr, thr, cys, gln, val, ser, leu, asn, his, phe, gly, ile, met In the diagram 4, green colour present serine residues of the protien. In the diagram 3, purple colour present the strand type of residues. In which light blue colour present conservative residues of protien. In this yellow and red colour present secondary structure of amino acid.ĭiagram 2 present helix type of amino acid. Thirdly, nucleotide sequence databases are much larger than protein databases because of the vast amounts of non-coding sequences coming out of eukaryotic genome projects, and this further lowers the search sensitivity.ĭiagram 1 present the normal secondary structure of the protein. Secondly, because of the redundancy of the genetic code, nearly one-third of the bases in coding regions are under a weak (if any) selective pressure and represent noise, which adversely affects the sensitivity of the searches. Thus, statistical significance can be ascertained for much shorter sequences in protein comparisons than in nucleotide comparisons. Firstly, because there are 20 amino acids but only four bases, an amino acid match carries with it >4 bits of information as opposed to only two bits for a nucleotide match. Emanual Michael Patelia*, Rakesh Thakur, Jayesh Patelĭepartment of Pharmaceutical analysis and chemistry (Gujarat technical university)ĭepartment of Pharmacology (University of acid sequence comparisons have several distinct advantages over nucleotide sequence comparisons, which, at least potentially, lead to a much greater sensitivity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
